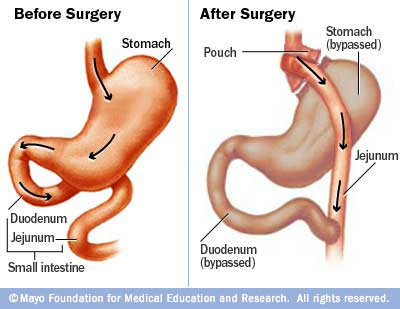
In gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y gastric bypass) the surgeon creates a small pouch at the top of your stomach and adds a bypass around a segment of your stomach and small intestine.
The surgeon staples your stomach across the top, sealing it off from the rest of your stomach. The resulting pouch is about the size of a walnut and can hold only about an ounce of food. The pouch is physically separated from the rest of the stomach. Then, the surgeon cuts the small intestine and sews part of it directly onto the pouch.
This connection redirects the food, bypassing most of your stomach and the first section of your small intestine, the duodenum (doo-o-DEE-num). Food enters directly into the second section of your small intestine, the jejunum (jay-JOO-num), limiting your ability to absorb calories. Even though food never enters the lower part of your stomach, the stomach stays healthy and continues to secrete digestive juices to mix with food in your small intestine.
Some surgeons perform this operation by using a laparoscope — a small, tubular instrument with a camera attached — through short incisions in the abdomen (laparoscopic gastric bypass). The tiny camera on the tip of the scope allows the surgeon to see inside your abdomen.
Compared with traditional "open" gastric bypass, the laparoscopic technique usually shortens your hospital stay and leads to a quicker recovery. Fewer wound-related problems also occur. Not everyone is a candidate for laparoscopic gastric bypass, however. Talk to your doctor about whether this approach is appropriate for you.
This entry was posted
on Wednesday, December 24, 2008
at 12:27 AM
. You can follow any responses to this entry through the
comments feed
.
About Me

- Matt Williams
- Newport News, Virginia, United States
- I am 29 years old. I had the Gastric Bypass and quit smoking on October 31, 2006. I am reborn!
How often do you exercise?
Archives
-
▼
2008
(17)
-
▼
December
(16)
- Workout #2
- 2 days of pain...
- Well, the fun starts today...
- Weight Loss Surgery: Pros and Cons...
- Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery Video...
- Gastric bypass surgery: Who is it for?
- Gastric bypass diet: What to eat after weight-loss...
- What are other weight-loss surgery options?
- What are the risks of gastric bypass surgery?
- What are the benefits of gastric bypass surgery?
- What can you expect after gastric bypass surgery?
- How is gastric bypass surgery done?
- Gastric bypass surgery: What can you expect?
- New Years Resolution...
- Are you thinking of getting the Bariatric Surgery?
- Becoming a Bariatric Nurse..
-
▼
December
(16)